I.About Foam
What is foam?

Causes of Foam Formation
(1)Use of surfactants: Surfactants, or surface-active agents, can contribute to foam formation due to their ability to reduce surface tension and stabilize bubbles.
(2)Use of high molecular weight compounds: Certain high molecular weight compounds, such as polymers, can contribute to foam formation due to their surface-active properties.
(3)Inherent foam-forming capability: Some substances have inherent foam-forming properties, but their rate of foam formation is higher than their ability to defoam.
(4)Mechanical agitation in viscous systems: In systems with high viscosity, such as during production or processing involving stirring or mixing, the entry of air can lead to bubble formation.
(5)Gas generation during chemical reactions: The occurrence of chemical reactions in a system can result in the generation of gas molecules, which is sometimes referred to as degassing or gas absorption process.
Why Defoaming?
(1)Prevention of material overflow: Foam can cause the overflow of reaction materials from the reaction vessel, resulting in wastage of raw materials and reducing production capacity.
(2)Improved collision between raw materials: Insufficient collision between raw materials due to foam can prolong the reaction cycle.
(3)Preservation of product quality: Foam formation can lead to a decline in product quality by trapping impurities or interfering with desired chemical reactions.
(4)Prevention of operational hindrances: The generation of foam can disrupt normal production processes, causing operational difficulties.
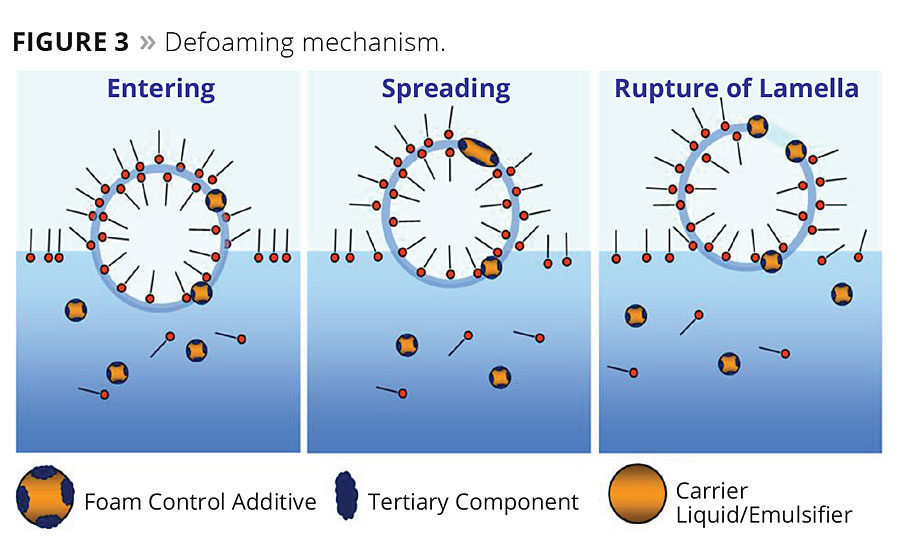
II. Defoaming Mechanism
The defoaming mechanism is as follows:
Defoamers have a low surface tension, which allows them to easily enter and spread within the liquid film. They reduce the surface tension of the liquid film, causing it to gradually thin out and become unevenly stressed. As a result, the liquid film loses its self-healing capability and eventually ruptures.
III. Classification, Characteristics, and Composition of Defoamers
Classification:
- Silicone-based defoamers
- Polyether-based defoamers
- Mineral oil-based defoamers
- Fatty alcohol-based defoamers
Solid defoamers
(2)Characteristics: Polyether-based defoamers exhibit excellent defoaming properties and high temperature resistance. However, they have certain toxicity, usage conditions are temperature-limited, and their defoaming speed is not very high, resulting in a narrow range of applications. Commonly found polyether-based defoamers in the market include GP type - glycerin polyoxypropylene ether, GPE type - polyoxypropylene-polyoxyethylene glycerol ether, and GPES type - polyoxypropylene-polyoxyethylene glycerol ether ester.
Silicone-based defoamers are primarily composed of polydimethylsiloxane, a liquid with extremely low surface tension. Fillers such as silica are added to form the main defoaming components, which can be prepared as emulsion-type or solid-type defoamers. Their key features include chemical stability, wide range of applications, low volatility, non-toxicity, and prominent defoaming ability. However, they may exhibit weaker defoaming performance as a drawback.




