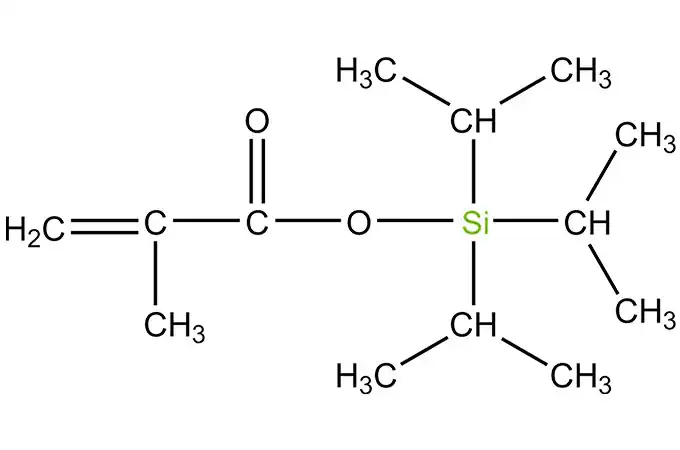
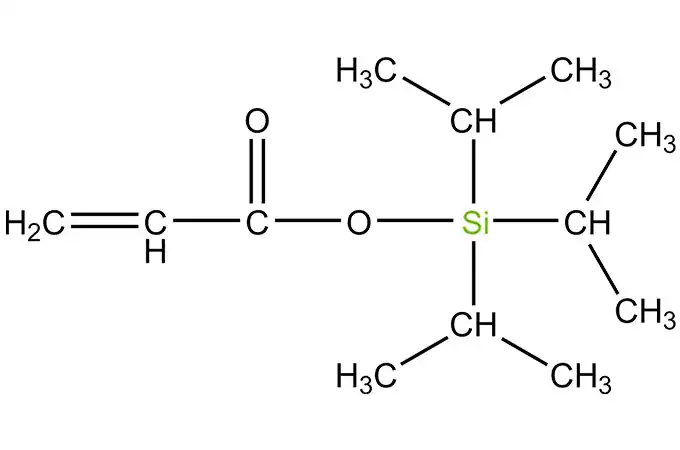
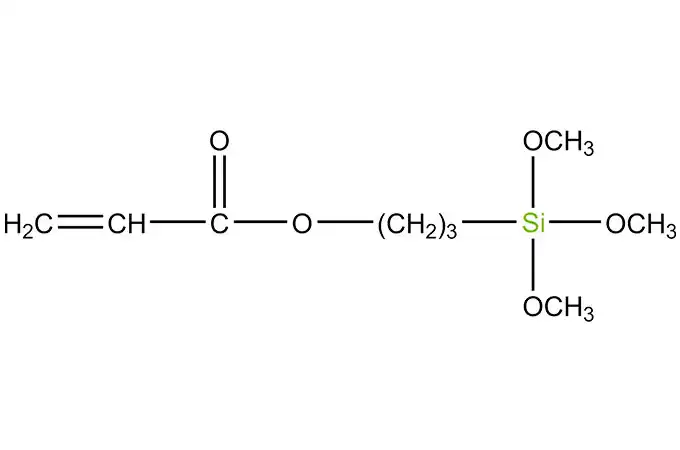
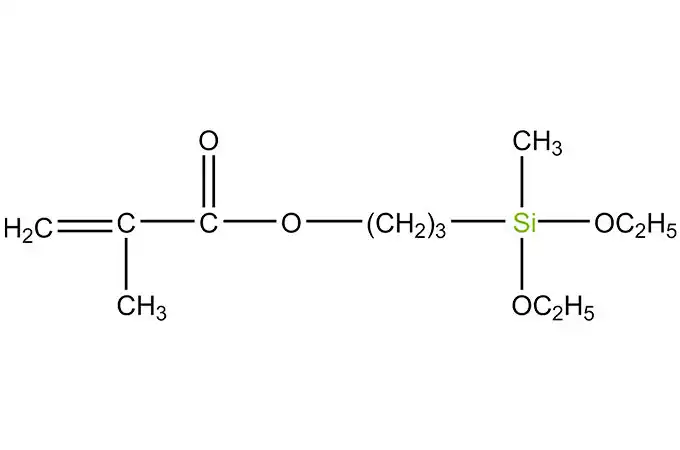
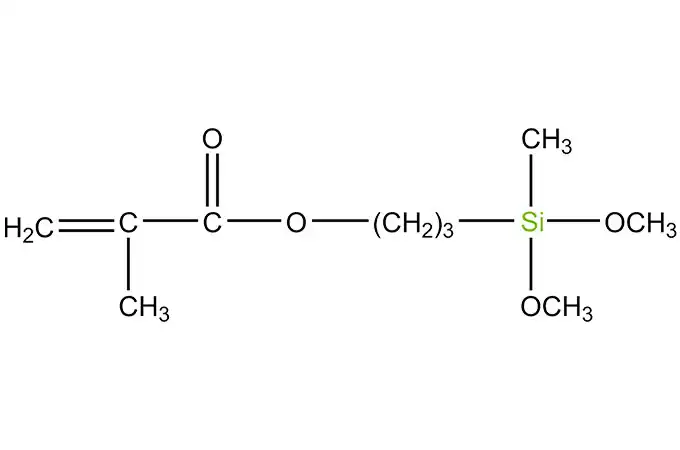
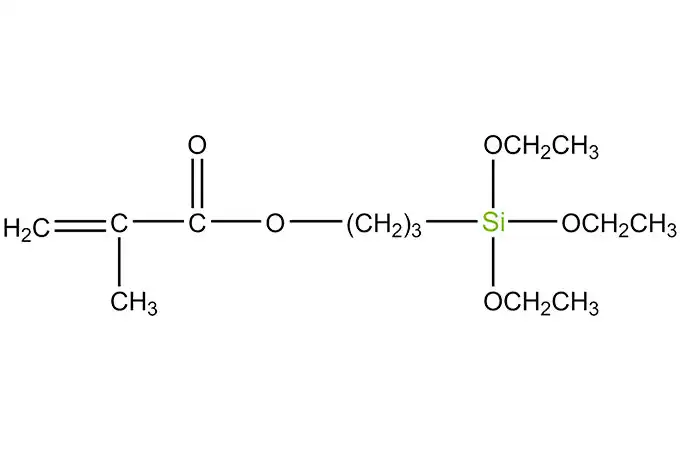
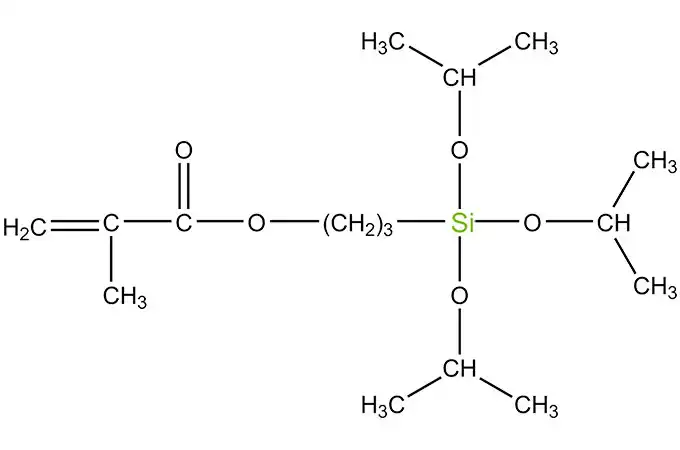
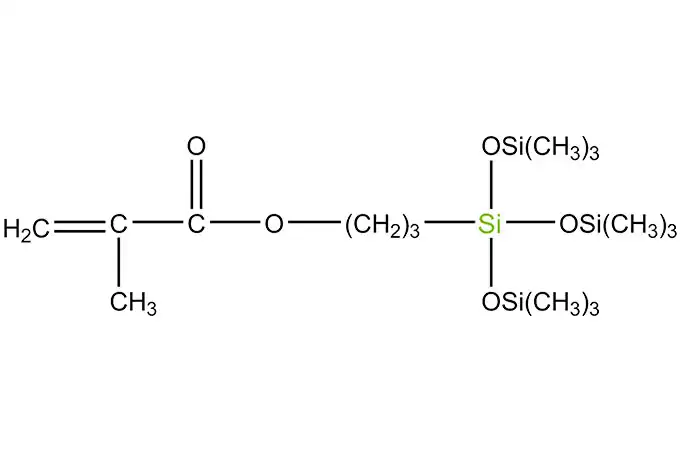
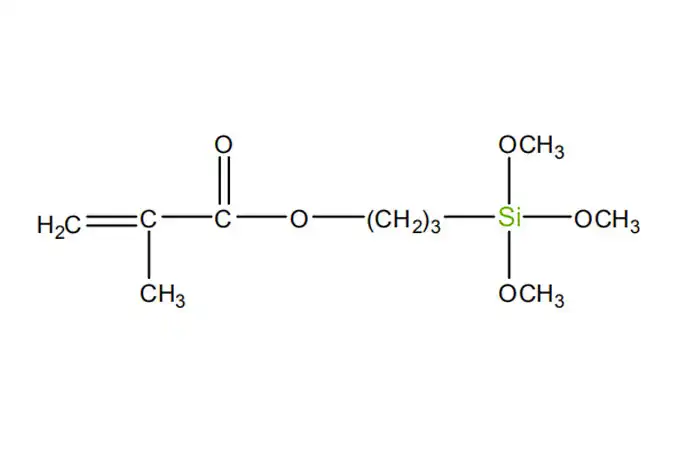
Acyl silanes are a class of organosilicon compounds that have a wide range of industrial applications. These compounds are characterized by the presence of acyl groups, which are bonded to silicon atoms. The acyl groups can be either aliphatic or aromatic, and they can vary in size and structure.
One of the primary applications of acyl silanes is in the production of silane-modified polymers (SMPs). These polymers are used as adhesives, sealants, and coatings. Acyl silanes are added to the polymer mixture to improve its adhesive properties, such as bonding to various substrates and resistance to moisture and chemicals.
Acyl silanes also have applications in the synthesis of functionalized silicas. These silicas have a wide range of applications, including as catalysts, adsorbents, and fillers in various industries.
The synthesis of acyl silanes involves the reaction of acyl chlorides with organosilanes, such as trialkoxysilanes or alkoxysilanes. The reaction is typically carried out in the presence of a catalyst, such as a tertiary amine or an organometallic compound.
In addition to their industrial applications, acyl silanes have also been studied for their potential use in organic synthesis. They have been shown to be effective in a range of reactions, including the acylation of alcohols and amines, as well as in the synthesis of beta-lactams.
In conclusion, acyl silanes are important compounds with a range of applications in various industries, including adhesives, coatings, and catalysis. The synthesis of these compounds requires specialized techniques and equipment, but they offer unique properties that make them valuable in many applications.