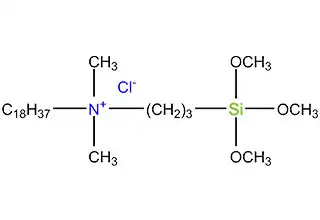
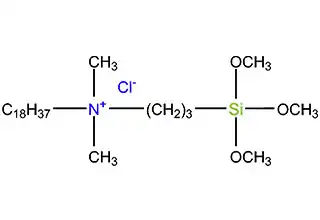
Antimicrobial silanes refer to a class of organic compounds that contain both silicon and antimicrobial groups, which are used to prevent the growth of microorganisms on various surfaces. These silanes are widely used in various industries, including healthcare, food processing, and water treatment.
One of the primary applications of antimicrobial silanes is in the production of antimicrobial coatings for medical devices and surfaces. The addition of these silanes to the coating mixture enhances its antimicrobial properties, making it effective against a wide range of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Antimicrobial silanes are also used in the food processing industry to prevent the growth of bacteria and other microorganisms on food contact surfaces. They are added to various materials, such as plastic and rubber, to make them resistant to microbial growth and reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses.
In addition, antimicrobial silanes are used in water treatment to prevent the growth of algae and other microorganisms in water storage tanks and pipelines. They are added to the water treatment chemicals to enhance their effectiveness against microbial growth.
However, the use of antimicrobial silanes has also raised concerns about their potential impact on human health and the environment. Some studies have suggested that the long-term exposure to these compounds may have adverse effects on human health, such as respiratory problems and skin irritation. Additionally, the release of these compounds into the environment may have negative effects on aquatic life.
In conclusion, antimicrobial silanes are an important class of compounds that have found widespread use in various industries to prevent the growth of microorganisms on surfaces. However, their potential impact on human health and the environment should be carefully considered, and efforts should be made to minimize their use and find alternatives that are less harmful.